Regular and Irregular Verbs: Definition, Rules, Examples
This article explains regular and irregular verbs and clarifies the differences between them. With clear explanations and examples, the article helps readers use verbs correctly in speaking and writing.
Regular and Irregular Verbs
What are the rules of regular and irregular verbs? We will learn the distinction and provide examples of each. They are essential part of English grammar.
What are Regular Verbs?
Regular verbs add “-ed,-d, -ied” to form the past tense and participles, which makes learning simpler and communication clearer. For example, “talk” changes to “talked,” allowing speakers to focus on their ideas rather than worrying about verb forms.
Regular verbs also encourage creativity in writing, helping with rhythm in prose and poetry. Understanding regular verbs improves grammar skills and helps express thoughts and feelings effectively.
What are Irregular Verbs?
Irregular verbs in English don’t follow the usual rules for changing forms. Irregular verbs have unique forms. This can be tough for learners, but it also makes learning English more interesting.
To understand these verbs, you need to do more than memorize them; you should look into their history in Old English and see how they have changed over time. Each irregular verb tells a story about how it has been used, which adds richness to the language.
Difference between Regular and Irregular Verbs
Knowing regular and irregular verbs helps improve English grammar.
| Regular Verbs | Irregular Verbs |
| Regular verbs have clear patterns, usually adding “-ed” for the past tense. | Irregular verbs do not follow these rules, which can confuse learners. |
| For example, “walk” becomes “walked” and “play” becomes “played.” | They can change completely, like “go” to “went” or “sing” to “sang.” |
| This consistency gives learners a sense of achievement. | This unpredictability shows the rich history of English. |
| Common sound structures in words | Uncommon sound structures in words |
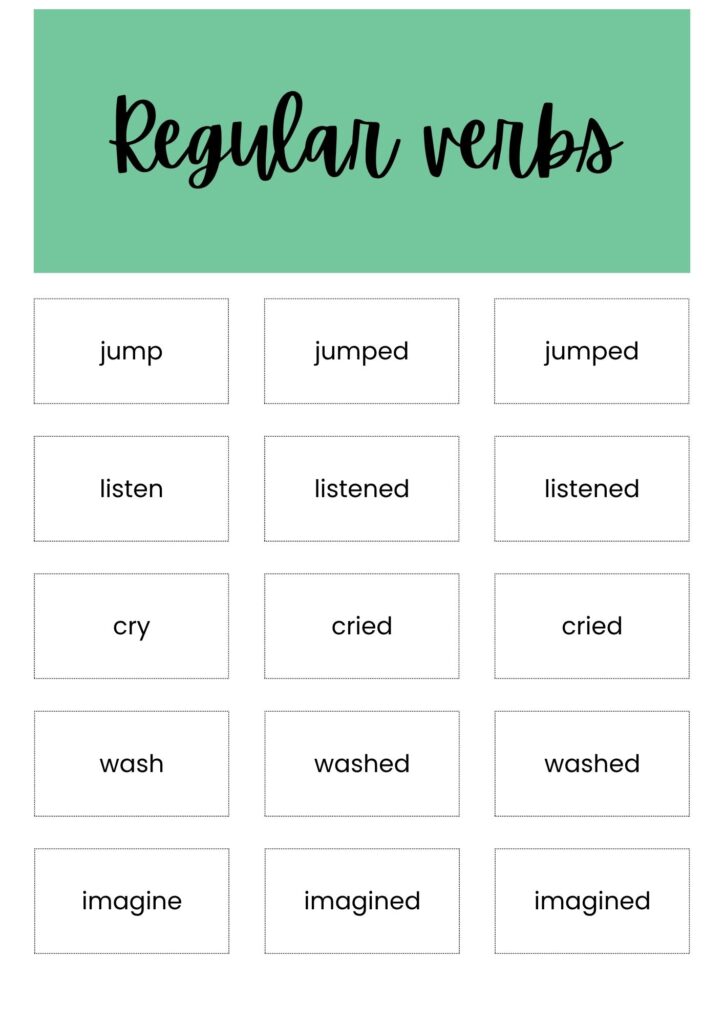
Examples of Regular Verbs:
| Base Form | Past Simple | Past Participle |
| walk | walked | walked |
| play | played | played |
| study | studied | studied |
| clean | cleaned | cleaned |
| listen | listened | listened |
| jump | jumped | jumped |
| agree | agreed | agreed |
| marry | married | married |
| hurry | hurried | hurried |
| plan | planned | planned |
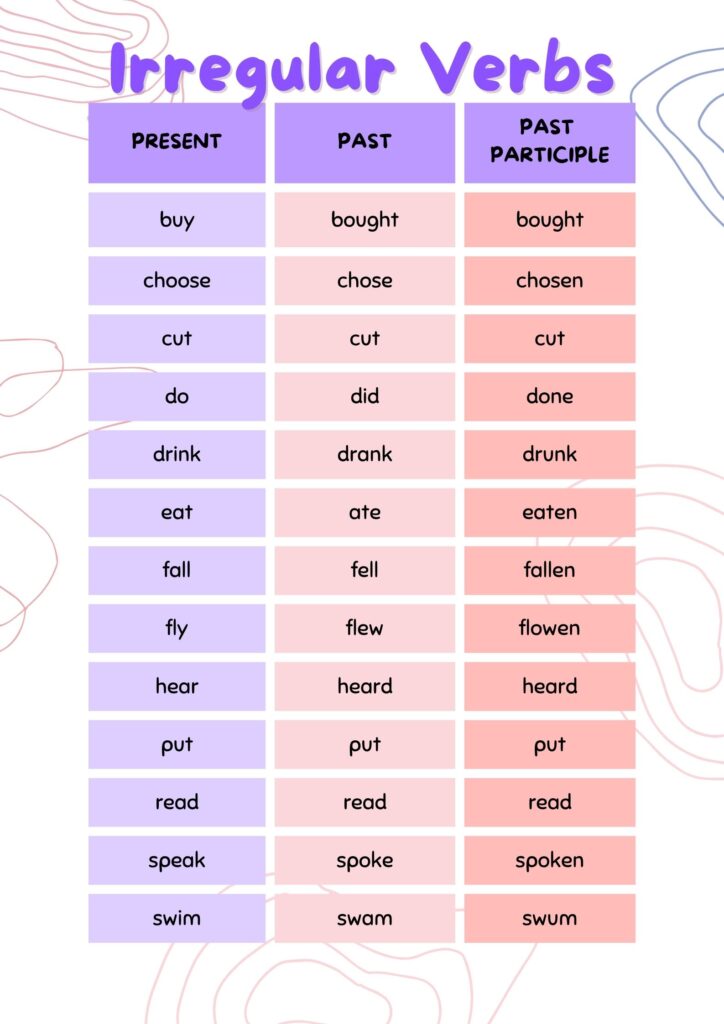
Examples of Irregular Verbs:
| Base Form | Past Simple | Past Participle |
| go | went | gone |
| eat | ate | eaten |
| write | wrote | written |
| see | saw | seen |
| make | made | made |
| pay | paid | paid |
| bleed | bled | bled |
| draw | drew | drawn |
| bite | bit | bitten |
| come | came | come |
Common mistakes with verb forms
Learning English verbs can be confusing because of regular and irregular forms. Regular verbs usually add “-ed” for the past tense, but some learners have trouble with spelling and pronunciation. For example, they might write “playd” instead of “played.”
Irregular verbs are even trickier, leading to mistakes like “goed” instead of “went.” This happens when learners try to use regular rules for all verbs. Auxiliary verbs can also cause problems; for instance, saying “I have went” instead of “I have gone” is incorrect.
Are there many irregular verbs in English?
Yes, there are many irregular verbs in English, and they often have unique forms that need to be memorized since they do not follow a single rule.
How do I remember irregular verbs?
To remember irregular verbs, group them by similar patterns (like sing–sang–sung), and practice regularly using flashcards or simple sentences. Reading and listening to English also helps you remember them naturally.
Are there verbs that can be both regular and irregular?
Yes, some verbs can be both regular and irregular. For example, learn can be learned (regular) or learnt (irregular), and both forms are correct.