Masculine And Feminine Gender
Knowing the differences between masculine and feminine forms in English can help you communicate better and make your writing clearer. In this article, the concept of gendered nouns and pronouns in English grammar will be explored, which often gets overlooked in a gender-neutral language. Through these distinctions, you’ll not only elevate your writing but also gain a deeper appreciation.
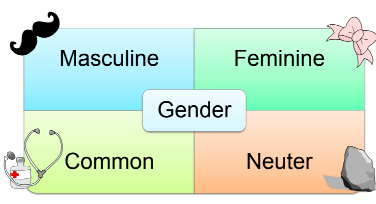
Defining Masculine and Feminine Gender:
Masculine gender refers to nouns and pronouns typically associated with male beings or have a masculine grammatical form.
Example: Boy, He, Grandfather
Feminine gender refers to nouns and pronouns typically associated with female beings or have a feminine grammatical form.
Example: Girl, Women, Sister
These genders don’t always correspond to biological sex and often apply to objects as well. These definitions can vary by culture and time and are increasingly understood as flexible and not fixed to biological sex.
Examples of Masculine and Feminine Gender:
Here’s a list of some examples of masculine and feminine in English. These are grouped in pairs for clarity.
| Masculine | Feminine | Masculine | Feminine |
| Actor | Actress | Boy Scout | Girl Guide |
| Prince | Princess | King | Queen |
| Father | Mother | Hero | Heroine |
| Nephew | Niece | Emperor | Empress |
| Husband | Wife | Duke | Duchess |
| Tiger | Tigress | Sultan | Sultana |
| Lion | Lioness | Businessman | Businesswoman |
| Host | Hostess | Congressman | Congresswoman |
| Salesman | Saleswoman | Actor | Actress |
| Steward | Stewardess | Mayor | Mayoress |
| Shepherd | Shepherdess | Count | Countess |
| Czar | Czarina | Host | Hostess |
| Patron | Patroness | Proprietor | Proprietress |
| Jew | Jewess | Benefactor | Benefactress |
| Manservant | Maidservant | Nephew | Niece |
| Emperor | Empress | Beau | Belle |
| Father-in-law | Mother-in-law | Bachelor | Spinster |
| Son-in-law | Daughter-in-law | Male | Female |
| Brother-in-law | Sister-in-law | Grandfather | Grandmother |
| Cavalier | Damsel | Stepbrother | Stepsister |
| Lord | Lady | Godson | Goddaughter |
| Fisherman | Fisherwoman | Policeman | Policewoman |
| Chairman | Chairwoman | Gander | Goose |
| Fireman | Firewoman | Mayor | Mayoress |
| Duke | Duchess | Gentleman | Gentlewoman |
| Count | Countess | Lord | Lady |
| Baron | Baroness | Stallion | Mare |
| Master | Mistress | Actor | Actress |
| Proprietor | Proprietress | Buck | Doe |
| Poet | Poetess | Bull | Heifer |
| Host | Hostess | Dog | Bitch |
| Ram | Ewe | Monk | Nun |
| Drake | Duck | Priest | Priestess |
| Boar | Sow | Bachelor | Bachelorette |
| Drone | Bee | Sultan | Sultana |
| Prince | Princess | Signore | Signora |
| Bridegroom | Bride | Drake | Duck |
| Poet | Poetess | Gander | Goose |
| Actor | Actress | Boar | Sow |
| Mr. | Mrs. | Waiter | Waitress |
| Master | Mistress | King | Queen |
| Landlord | Landlady | Monk | Nun |
| Son | Daughter | Wizard | Witch |
| Bull | Cow | Wizard | Witch |
| Dog | Bitch | Uncle | Aunt |
| Rooster | Hen | Heir | Heiress |
| Stallion | Mare | Horse | Mare |
| Monk | Nun | Ram | Ewe |
| Gentleman | Lady | Fox | Vixen |
Common Gender-Neutral Terms:
Here are common gender-neutral terms that can be used instead of gendered ones, grouped by category:
1. People / Titles
- Actor/Actress Actor
- Waiter/Waitress Server
- Steward/Stewardess Flight attendant
- Policeman/Policewoman Police officer
- Fireman/Firewoman Firefighter
- Chairman/Chairwoman Chairperson / Chair
- Businessman/Businesswoman Businessperson
- Salesman/Saleswoman Salesperson
- Congressman/Congresswoman Legislator / Representative
- Mankind Humanity / Humankind
- Manpower Workforce / Staff
- Landlord/Landlady Property owner / Manager
2. Family / Relationships
- Father/Mother Parent
- Son/Daughter Child
- Brother/Sister Sibling
- Husband/Wife Spouse
- Boyfriend/Girlfriend Partner / Significant other
- Uncle/Aunt Pibling (informal), Parent’s sibling
- Nephew/Niece Nibling (informal)
- Father-in-law/Mother-in-law Parent-in-law
- Godfather/Godmother Godparent
3. General Terms
- Man Person / Individual
- Gentleman/Lady Guest / Patron / Person
- Hero/Heroine Hero (neutral usage now)
- King/Queen (contextual) Ruler / Monarch
- Lord/Lady Noble / Titleholder
These alternatives promote inclusive language and can be helpful in both formal and casual settings.
The Role of Masculine and Feminine Gender in Language:
Gender affects language in many ways, not just through pronouns or titles. It influences how we see and interact with each other in society. Language can show and support gender expectations, which can affect how people view authority and skills. Studies have shown that when women use assertive language, they may be perceived as aggressive, while men using the same language are often seen as confident.
Also, using gender-inclusive language is important for creating fair conversations. By accepting these changes, we acknowledge the fluidity of gender and the importance of language in shaping social reality.
Basic rules for writing Masculine and Feminine Gender:
Here’s a basic list of rules and guidelines for gender-inclusive writing, often called gender-sensitive writing:
1. Use Gender-Neutral Terms
Avoid: policeman, chairman, fireman
Use: police officer, chairperson/chair, firefighter
2. Avoid Assuming Gender
Avoid: Each student must bring his own lunch.
Use: Each student must bring their own lunch.
3. Use “They” as a Singular Pronoun
Acceptable in modern usage for unknown or nonbinary gender.
Example: Someone left their phone on the table.
4. Address All Genders Equally
When referring to groups, use inclusive language.
Avoid: Ladies and gentlemen (unless formal context)
Use: Everyone, all attendees, guests
5. Avoid Gender Stereotypes
Don’t assign roles, traits, or expectations based on gender.
Avoid: Women are more emotional; men are strong.
Use: Use individual-specific descriptions when needed.